| |
 |
| |
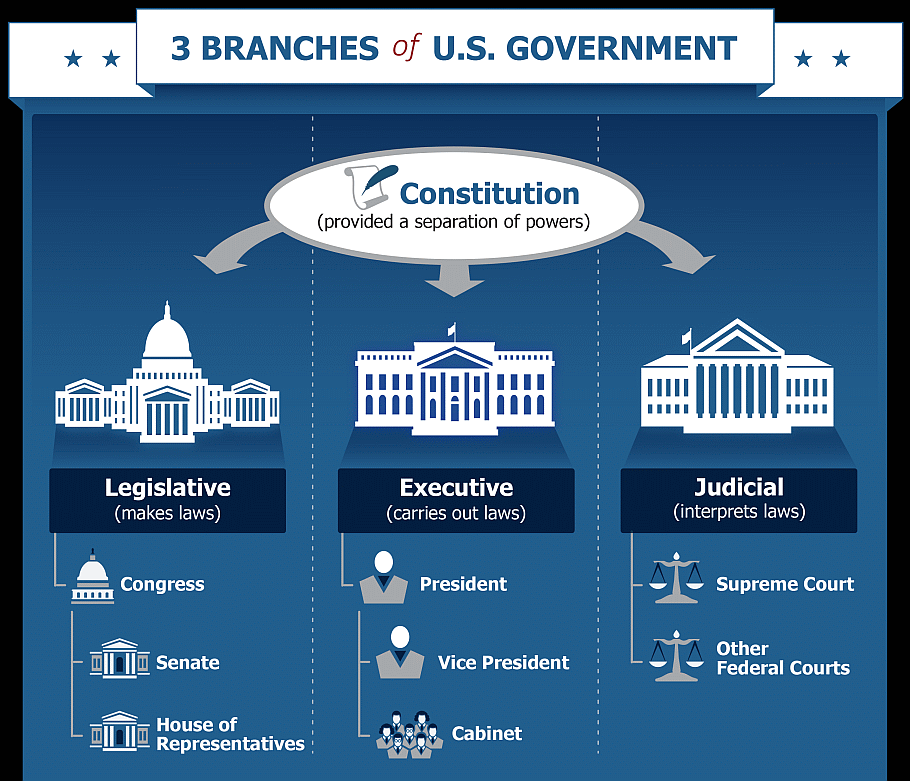
| The U.S. government is a representative democracy with two legislative bodies. These bodies are the Senate and House of Representatives. The Senate consists of 100 seats with two representatives from each of the 50 states. The House of Representatives consists of 435 seats and are elected by the people from the 50 states. The executive branch consists of the President who is also the head of government and chief of state.
The President of the United States is the head of state of the U.S., the chief executive of the federal government, and Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces. The United States was the first nation to create the office of President as the head of state in a modern republic.
The Constitution requires the President to give Congress a State of the Union, which is a report that addresses a President's legislative proposals and other plans for the country. There is no requirement stating what form or how often the report occurs; however, it normally occurs annually in the last week of January. |
| |
| LEGISLATIVE |
The legislative branch drafts proposed laws, confirms or rejects presidential nominations for heads of federal agencies, federal judges, and the Supreme Court, and has the authority to declare war. This branch includes Congress (the Senate and House of Representatives) and special agencies and offices that provide support services to Congress. American citizens have the right to vote for Senators and Representatives through free, confidential ballots.
Congress confirms or rejects the president's nominees and can remove the president from office in exceptional circumstances.
- Senate - There are two elected Senators per state, totaling 100 Senators. A Senate term is six years and there is no limit to the number of terms an individual can serve.
- House of Representatives - There are 435 elected Representatives, which are divided among the 50 states in proportion to their total population. There are additional non-voting delegates who represent the District of Columbia and the territories. A Representative serves a two-year term, and there is no limit to the number of terms an individual can serve.
|
| Members of the U.S. Congress |
| Capitol Hill Facts |
| |
| EXECUTIVE |
The executive branch carries out and enforces laws. It includes the President, Vice President, the Cabinet, executive departments, independent agencies, and other boards, commissions, and committees.
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the President of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C. and has been the residence of every U.S. President since John Adams in 1800.
The president leads the country. He or she is the head of state, leader of the federal government, and Commander in Chief of the United States Armed Forces. The president serves a four-year term and can be elected no more than two times. The president can veto legislation created by Congress and nominates heads of federal agencies.
Key roles of the executive branch include:
- President - The president leads the country. He or she is the head of state, leader of the federal government, and Commander in Chief of the United States Armed Forces. The president serves a four-year term and can be elected no more than two times. The president can veto legislation created by Congress and nominates heads of federal agencies.
- Vice President - The vice president supports the president. If the president is unable to serve, the vice president becomes president. The vice president can be elected and serve an unlimited number of four-year terms as vice president, even under a different president.
- The Cabinet—Cabinet members serve as advisors to the president. They include the vice president, heads of executive departments, and other high-ranking government officials. Cabinet members are nominated by the president and must be approved by a simple majority of the Senate—51 votes if all 100 Senators vote.
The First Lady of the United States has traditionally been the wife or other close female relative of the President of the United States. First Ladies are the hostesses of the White House, serve as advisors to the President, and are often involved in social issues. Over the course of American history, the role of the First Lady has changed and evolved.
The Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of American History in Washington, DC, features a First Ladies exhibition, one of the museum's most popular attractions. Its virtual First Ladies interactive tour provides a visual experience of the First Ladies' gowns and other artifacts. |
| The White House |
| White House Facts |
| The Presidents |
| First Ladies of the United States |
| Presidential Greetings, Photographs, and Invitations |
| Data.gov - Public access to the Executive Branch |
| |
Order of Presidential Succession |
The U.S. Constitution and the Presidential Succession Act of 1947 give guidelines for the presidential order of succession.
If the President of the United States is incapacitated, dies, resigns, is for any reason unable to hold his/her office, or is removed from office, he/she will be replaced in the following order:
- Vice President
- Speaker of the House
- President Pro Tempore of the Senate
- Secretary of State
- Secretary of the Treasury
- Secretary of Defense
- Attorney General
- Secretary of the Interior
- Secretary of Agriculture
- Secretary of Commerce
- Secretary of Labor
- Secretary of Health and Human Services
- Secretary of Housing and Urban Development
- Secretary of Transportation
- Secretary of Energy
- Secretary of Education
- Secretary of Veterans Affairs
- Secretary of Homeland Security
|
| |
| JUDICIAL |
The judicial branch interprets the meaning of laws, applies laws to individual cases, and decides if laws violate the Constitution. It's comprised of the Supreme Court and other federal courts. The Justices of the Supreme Court, who can overturn unconstitutional laws, are nominated by the president and confirmed by the Senate.
- Supreme Court - The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States. The Justices of the Supreme Court are nominated by the president and must be approved by the Senate.
- Nine members make up the Supreme Court - a Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices. There must be a minimum or quorum of six Justices to decide a case.
- If there is an even number of Justices and a case results in a tie, the lower court's decision stands.
- There is no fixed term for Justices. They serve until their death, retirement, or removal in exceptional circumstances.
-
Federal Courts and Judicial Agencies – The Constitution gives Congress the authority to establish other federal courts to handle cases that involve federal laws including tax and bankruptcy, lawsuits involving U.S. and state governments or the Constitution, and more. Other federal judicial agencies and programs support the courts and research judicial policy.
|
| |
| Supreme Court of the United States |
| United States Courts |
| About the Court - Supreme Court of the United States |
| Five Things to Know About the Supreme Court |
|
|
